What Are SKU Codes and How to Create Them?
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce and retail, keeping track of inventory is no small feat. Whether you’re managing a single online store or juggling multiple marketplaces, one tool stands out as a cornerstone of efficient inventory management: the SKU code. But what exactly is an SKU code, and how can you create one that works for your business? Let’s break it down and explore actionable steps to craft effective SKU codes in 2025.
What Is an SKU Code?
SKU stands for Stock Keeping Unit. It’s a unique alphanumeric identifier assigned to each product or variation in your inventory. Think of it as a digital fingerprint that distinguishes one item from another, capturing key details like size, color, brand, or style. For example, a small red T-shirt and a medium blue T-shirt from the same brand would each have their own SKU code, allowing you to track their stock levels independently.
Unlike universal identifiers like UPC (Universal Product Code) or EAN (European Article Number), which are standardized globally and tied to barcodes, SKU codes are internal. This means you have the freedom to design them however you see fit, tailoring them to your business’s specific needs. Whether you’re a small retailer or a multi-channel seller, SKUs empower you to monitor stock, streamline operations, and ensure you’re never caught off guard by an unexpected shortage—or surplus.
Why SKU Codes Matter in 2025
In today’s omnichannel retail landscape, where businesses sell across platforms like Amazon, Shopify, Flipkart, and physical stores, SKU codes are more critical than ever. They help you:
- Track Inventory Accurately: Know exactly how many units of each product variation you have in stock.
- Simplify Multi-Channel Selling: Sync inventory across platforms to avoid overselling or stockouts.
- Boost Efficiency: Quickly locate items in your warehouse or database without digging through endless descriptions.
- Analyze Performance: Identify top sellers or slow movers with SKU-level data.
With tools like Ginesys OMS’s (Browntape) inventory management software, SKU codes can also integrate seamlessly with automation features—updating stock levels in real time and even generating printable barcodes for your products.
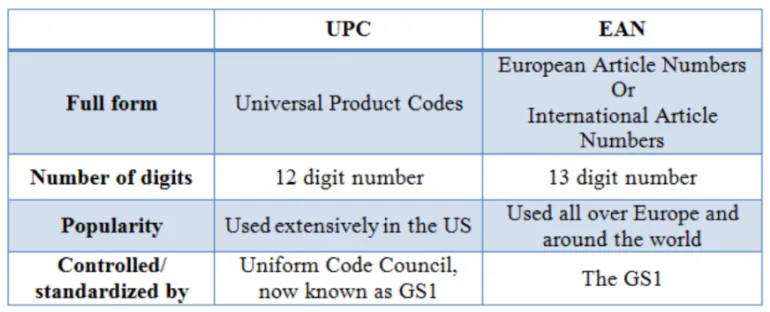
SKU vs. UPC vs. EAN Codes
While SKU codes are primarily for internal inventory management, UPC (Universal Product Code) and EAN (European Article Number) are standardized codes used globally. Here’s how they differ:
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) – Customizable, internal code for tracking inventory.
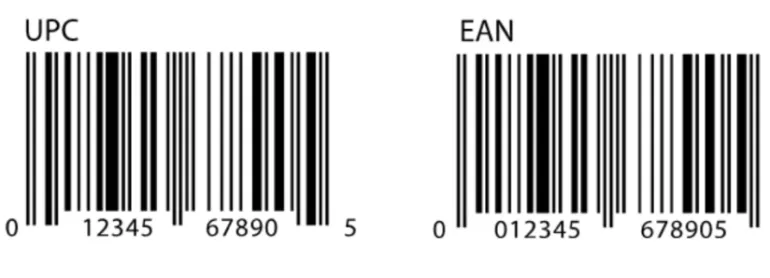
- UPC (Universal Product Code) – A 12-digit barcode used globally for retail product identification.
- EAN (European Article Number) – A 13-digit barcode primarily used outside North America for international trade.
UPC and EAN codes are regulated by GS1, an organization that issues unique codes to manufacturers. Retailers must apply for these codes, which often involve fees. In contrast, SKUs can be freely created and managed within a business.
What are UPC and EAN codes?
UPC or EAN are part of a barcode. They are unique identifiers for products. These codes are printed on most consumer goods, like electronics, clothing, accessories and other physical merchandise.
How are these significant for a product?
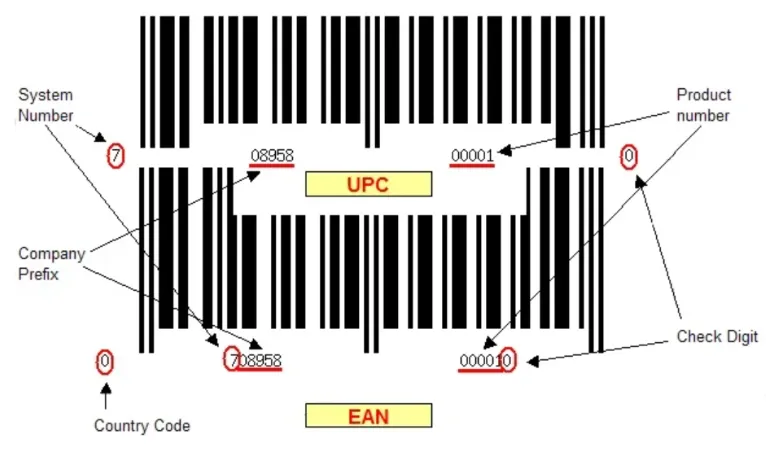
UPC/EAN codes help in distinguishing one product form others. These numbers are unique identification marks. They can represent details like:
- The type of product
- Its various features – price, weight or color
- Product manufacture
- Country codes
- Other product related data
UPC/EAN codes are printed on products and/or their packaging. The bars of the code are scanned and read by a computer. If the barcode cannot be scanned properly, the UPC/EAN code can be manually entered into a computerised system to derive product specifications. This makes it easy for manufacturers, suppliers and sellers to:
- Search and find products
- Verify whether the barcode was read properly
- Minimise human error during data entry and processing
- Eliminates decoding handwritten information and inconsistent labelling
The critical factor here is that the SKU codes must be well created – unique and humanly recognisable. That is, the user must be able to access all the relevant information about the product without confusion or misinterpretation through the code. So how does one go about creating good SKU codes? Let us find out through the 5 good tips that follow.
How to Create Effective SKU Codes
Ensuring each SKU code is unique for every product variant in your inventory is crucial. Additionally, following these best practices will make them more human-readable, easily decipherable, and seamlessly integrable into modern inventory management systems.
1. Create Your Own SKU Code Format
Avoid using manufacturer or wholesaler codes as part of your SKU. While it may seem convenient to modify an existing code by adding prefixes or suffixes, it can cause issues if you change suppliers in the future. Instead, develop a structured SKU format tailored to your business to maintain consistency and scalability.
2. Define the Information Your SKU Should Convey
Determine what essential details the SKU should represent. Overloading it with unnecessary data leads to complexity and potential misinterpretation. The SKU should be a clear, concise identifier. For example, if the manufacturing year is irrelevant for a product, store it separately in the system rather than including it in the SKU.
3. Follow a Logical Hierarchy (Cascade Method)
Design SKU codes using a structured, hierarchical approach. For instance, if you sell electronic devices from multiple brands, break down the SKU systematically:
- Category → ‘Electronics’ (E)
- Subcategory → ‘Laptops’ (L)
- Brand → Dell (DELL)
- Model & Specification → Latitude 5500, 16GB RAM, Silver (L5500-16-SLV)
Each attribute should add to the uniqueness of the SKU, ensuring no two products share the same code. To avoid ambiguity, use the first three letters of attributes instead of just one.
Example of Well-Structured SKU Codes:
Here are sample SKU codes describing Brand, Product, Color, and Size for apparel:
- ChicBrand Shirt Red Small – CHI-SHI-RED-S
- ChicBrand Shirt Red Medium – CHI-SHI-RED-M
- ChicBrand Shirt Blue Medium – CHI-SHI-BLU-M
- ChicBrand Shirt Black Medium – CHI-SHI-BLK-M** (Using 3-letter codes prevents misidentification.)
4. Choose Clear, Readable Fonts and Characters
Avoid characters that look similar (homoglyphs), such as:
- "O" (letter O) vs. "0" (zero)
- "I" (uppercase i) vs. "l" (lowercase L)
These can cause misreading and data entry errors. Use bold, easy-to-read fonts. Additionally, avoid symbols like /, $, or @, as these may cause formatting errors in inventory management software like Excel or ERP systems.
By following these guidelines, businesses can create SKU codes that are clear, scalable, and compatible with modern eCommerce and inventory management systems.
How to Register and Obtain UPC/EAN Codes? How Are They Generated?
Manufacturers typically provide UPC/EAN codes for their products. However, if a product does not come with these codes, online sellers must acquire them from GS1 (formerly known as EAN International). GS1 is the global authority that assigns unique company prefixes for generating barcodes used in supply chains. It operates in over 100 countries, making it the official source for UPC/EAN codes.
Can Products Be Sold Online Without UPC/EAN Codes?
UPC/EAN codes help streamline online selling by simplifying product identification and inventory management. While these codes are not mandatory, they are highly recommended. Marketplaces like Amazon, Flipkart, and others request sellers to enter these numbers while listing products.
What About Products Without UPC/EAN Codes?
Certain products, such as handicrafts, artwork, or customized goods, may not come with barcodes. If you’re selling such items, you can still list them online, but you may need to follow alternative methods, including:
Brand Registry: Required on platforms like Amazon and Flipkart. This process involves submitting legal documents such as trademark certificates and typically takes 1-2 weeks to complete. Once registered, there is no need for renewal.
UPC/EAN Exemption: If you don’t have a UPC/EAN, Amazon offers an exemption process. However, it takes about a month to process and is valid only for a limited period, requiring monthly renewal.
Are UPC/EAN Codes Required for All Product Categories?
UPC/EAN codes apply to all products, but they are not always compulsory. Categories that naturally lack barcodes can still be sold on marketplaces using the alternatives mentioned above.
How Many UPC/EAN Codes Do You Need?
Each variation of a product requires a unique UPC/EAN code. For example, if you sell apparel, you need separate UPC/EAN codes for different colors, patterns, sizes, and styles.
The Importance of SKU Codes in E-commerce
What Is an SKU Code?
SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) codes play a critical role in e-commerce operations, especially when selling across multiple platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra, Shopify, Magento, and offline stores.
Why Are SKU Codes Important?
Omnichannel Selling: Businesses often sell across multiple channels (online and offline). SKU codes ensure product consistency across all platforms.
Inventory Syncing: Maintaining synchronized inventory across digital platforms prevents out-of-stock errors, minimizes lost sales, and maximizes revenue.
Warehouse Efficiency: Barcode-integrated SKU codes enable faster order processing in warehouses by automating picking, packing, and shipping. Without SKU codes, warehouses rely on product images, which increases errors and leads to costly returns and replacements.
Using an Inventory Management System for SKU Codes
Instead of relying on spreadsheets, use an inventory management system to store and track SKU codes efficiently. Unlike Excel, which is prone to errors and data loss, an inventory management system automates and simplifies operations.
How Ginesys OMS (Browntape) Helps with SKU Management
Ginesys OMS (Browntape) inventory management system allows you to:
- Generate and print SKU barcodes for your products
- Map your SKU codes to those used by third-party marketplaces (Amazon, Flipkart, Magento, etc.)
- Automate inventory and price updates across all sales channels
- Sync inventory seamlessly across online and offline stores
In conclusion, SKU codes are an essential part of inventory management, ensuring smooth e-commerce operations. If you need assistance, Ginesys OMS (Browntape) is here to help you optimize your inventory and sales.
Ready to enhance your e-commerce efficiency? Contact us today!